The car seat safety sensor is a thin-film contact sensor with contacts evenly distributed on the stress-bearing surface of the seat. When the seat is subjected to external pressure, the sensor generates a trigger signal.
The working principle of the car seat safety sensor is mainly based on pressure sensing and position detection. For the occupancy sensor, a pressure-sensitive chip is usually installed inside it. When the seat is subjected to pressure, the chip detects the change in pressure and generates a corresponding electrical signal. After these signals are processed, it can be determined whether someone is sitting on the seat.
car seat safety sensors have a wide range of applications and functions in cars, including but not limited to:
Seat belt alarm: When the seat sensor detects that someone is sitting on the seat, the seat belt alarm device will be triggered to remind the passenger to fasten the seat belt.
Airbag sensing: The seat sensor can also be used to detect the position and weight of the passenger on the seat, so as to adjust the inflation volume and deployment speed of the airbag in the event of a collision, providing more accurate safety protection.
Driver departure detection: When the driver leaves the seat, the sensor detects this action and automatically returns the vehicle to neutral or shuts down the engine to improve the safety of the vehicle.
Memory seat function: When used with position sensors, it can realize automatic adjustment and storage of seat positions, providing drivers with a more personalized driving experience.
The production process of automotive seat sensor membrane switches involves several key steps:
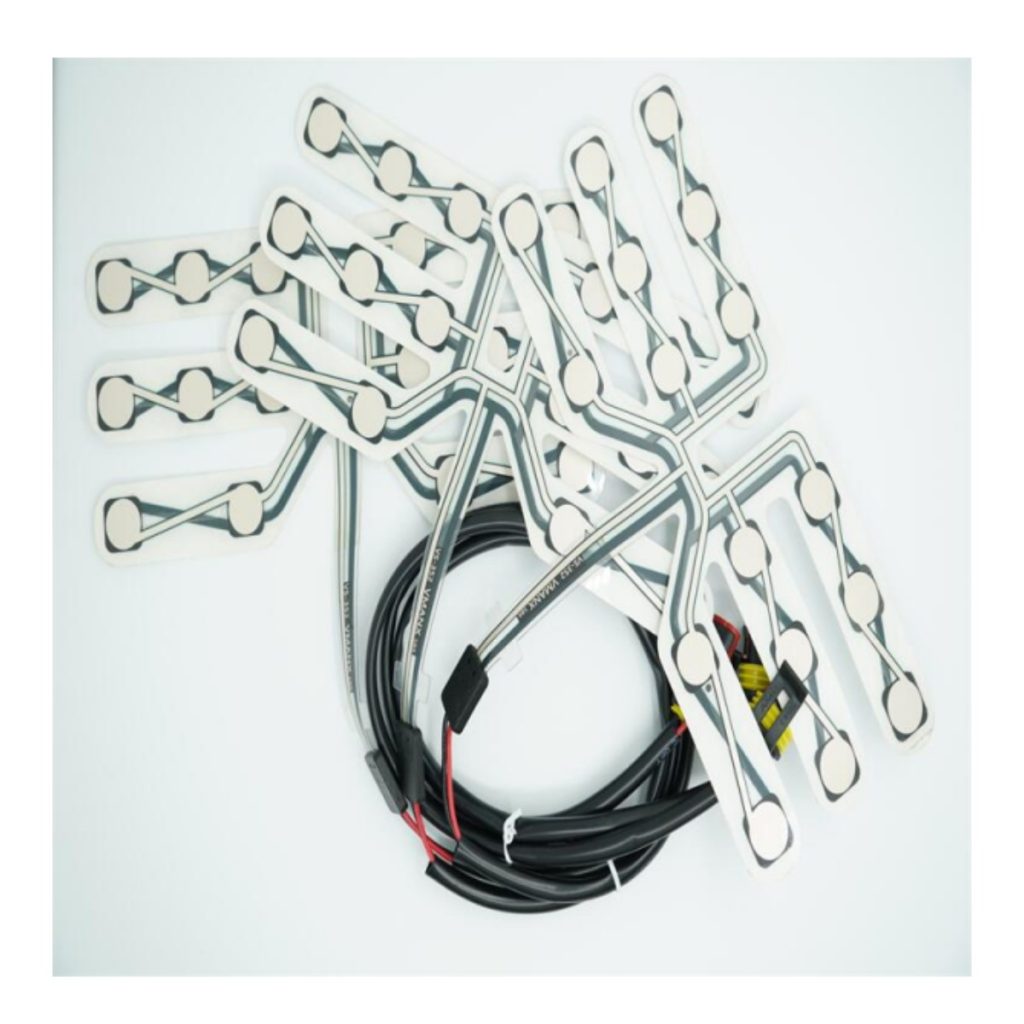

1. Prepare materials
Conductive materials: used to make circuits and electrodes, requiring good conductivity.
Insulating materials: used to form an insulating layer to prevent short circuits between conductive materials.
Supporting materials: used to enhance the structural strength and stability of membrane switches, soft, wear-resistant, and high-temperature resistant materials must be selected.
2. Design and production layout
Use design software: According to the design requirements of membrane switches, design circuit diagrams, conductive patterns, insulating patterns, etc.
Proofing confirmation: Proofing and confirming the designed layout to ensure that it meets the design requirements.
3. Conductive material cutting
Laser cutting or chemical etching: According to the designed conductive pattern, use laser cutting or chemical etching and other technologies to cut the conductive material into the desired shape.
Conductive and thermal conductivity testing: Ensure that the conductive material after cutting has good conductive and thermal conductivity.
4. Printing insulating layer
Printing technology: Print the insulating material on the conductive material to form an insulating layer.
Quality inspection: Ensure that the thickness of the insulating layer is uniform and of good quality to avoid short circuits between conductive materials.
V. Assembly and connection
Paste support materials: Paste the support materials on the insulating layer to enhance the structural strength and stability of the membrane switch.
Assemble components: Assemble the manufactured components together according to the design requirements, including circuit film, insulating layer, support materials, etc.
Electrical connection: Make electrical connections to ensure that the circuit connections between the components are correct.
VI. Pressure sensing layer production and packaging
Printed resistor layer: Print the resistor layer on the insulating film layer and locate it in the clamping area. The material of the resistor layer can include carbon black, graphite and resin, etc., and the parameters such as resistivity and printing thickness must meet the design requirements.
Wire connection: Short-circuit the resistor layer to connect the two wires located in the wiring area.
Film bonding: Bond the two circuit films to each other so that the pressure-sensing electrodes on the two inner surfaces are aligned with each other, and the resistor layer is sandwiched between the insulating film layers of the two circuit films.
Plastic block sealing: On the lead side of the membrane switch sheet, use a plastic block to seal the solder joints to enhance waterproofness and solder joint bonding strength. The plastic seal block can be sealed with a dispensing method or injection molding method that is easy to form.
VII. Functional test and appearance inspection
Functional test: Perform functional tests on the completed membrane switch to ensure that the sensor can accurately sense pressure and transmit signals.
Appearance inspection: Check whether the appearance of the membrane switch is flat and flawless to ensure that the product quality is qualified.
car seat safety sensors play a vital role in modern cars. They not only improve driving comfort and convenience, but also enhance vehicle safety. Therefore, they need to be given enough attention and care during use and maintenance.